Hibernation mode is also known as suspend to disk or safe sleep on computers. It’s the simple movement of memory stored on the RAM (which deals with all the basic activities carried out in the computer).
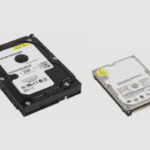
The memory from the RAM is shifted onto the hard disk. Once the computer is turned on, the memory is restored to the RAM, and the computer is exactly as it was before entering hibernation mode. It was first implemented in 1992 and patented by Compaq computer corporation in Huston, Texas.
Hibernation is mainly used in laptops that have a limited battery power supply. Some desktops also make use of this mode mostly as a form of energy-saving measures or for quick replacement of batteries safely.
Which Operating Systems Support Hibernation Mode
Microsoft
Most modern operating systems make use of hibernation mode. Operating systems like Microsoft all make use of hibernation mode on all their hardware devices and plug-and-play systems. In the event of a power failure, some desktops make use of the speed of their SSD’s to hibernate quickly to prevent the loss of data. All forms of windows have made use of hibernation mode right from windows 95 to 10 pro.
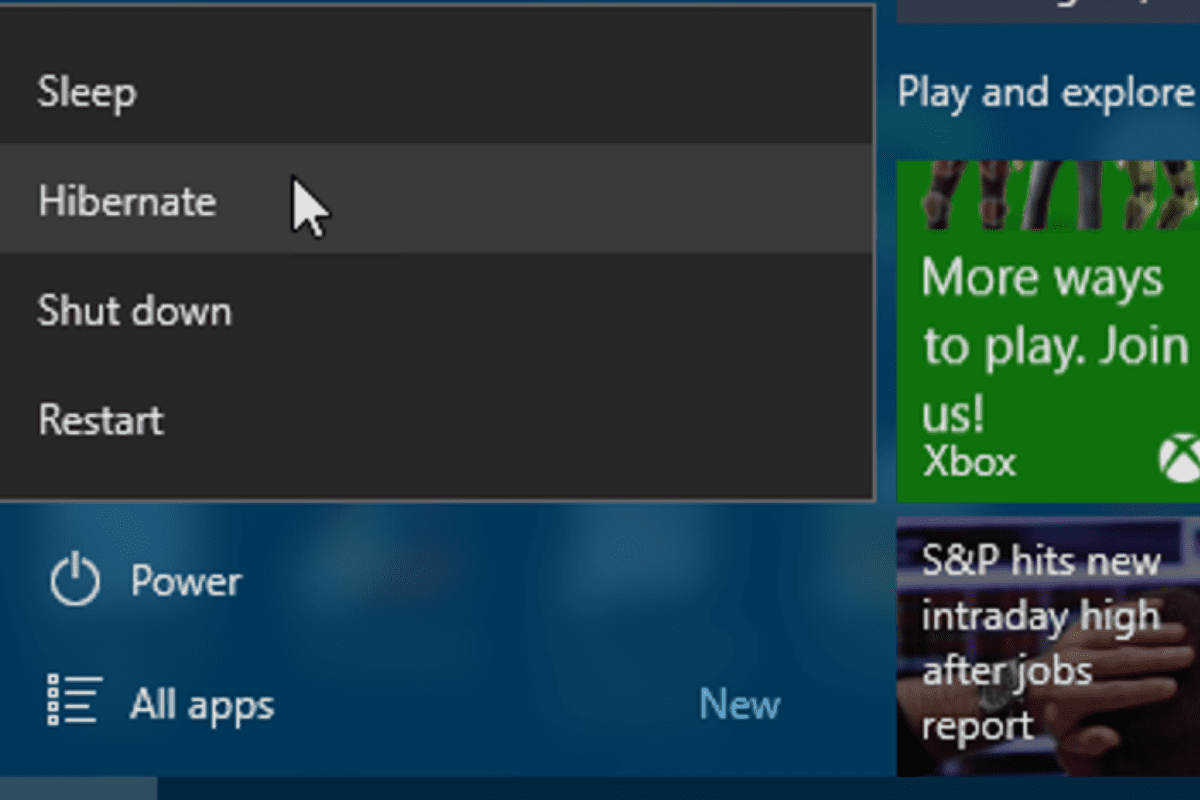
Windows 8 uses a multi-core resume-from-hibernation mode algorithm that has been optimised for Windows 10 and the pro version as well. It also introduced a fast startup feature. Whenever a user makes use of the shutdown option, it is actually hibernating but closing all applications. However, users may perform a traditional shutdown by holding down the shift key while clicking shut down.

Apple Computers
On MAC the same procedure is carried out but only with a slight difference as it takes all volatile memory instead of just what is stored on the RAM. However, in the event of a power failure, the MAC would wake up from a “safe sleep” instead, it restores memory content from the hard disk. This is because the “safe sleep” hibernation process occurs during regular sleep, and the Apple menu does not have a hibernation mode. It was added to all Mac models in October 2005 and was a firmware update from the same period. It requires Mac OS X v 10.4 or higher to be activated.

Linux
The Linux kernel implements its hibernation mode by “swsusp ” which was built into its 2.6 series and it is referred to as “suspend-to-disk mode”. It has an alternative model which makes use of patch update 3.4 on Tuxonlce and provides advantages such as symmetric-multiprocessing and preemption. Or another alternate implementor like “uswsusp“.
Sleep Mode vs Hibernation Mode
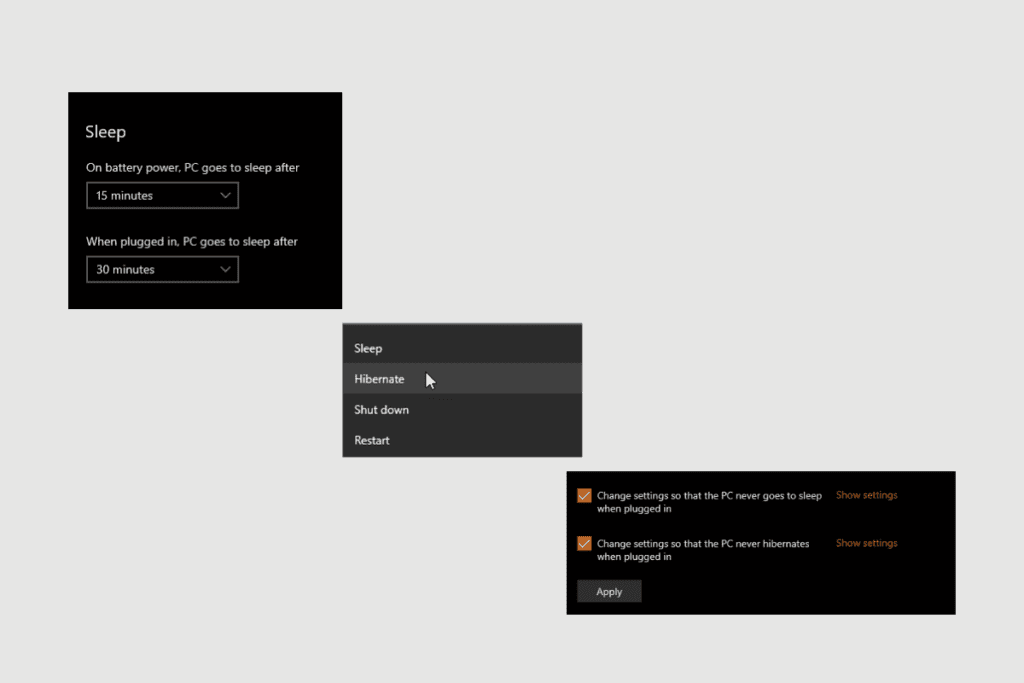
Most systems make use of a low-power sleep mode in which the processing function of said system is lowered as it uses less than a third of the power to preserve the contents of the RAM, which creates the bases for a fast start-up.
This is where hibernation and sleep mode differ. The basis of both modes is on how we can keep all the functions of the RAM, i.e. all the apps we are using, remain open, but our laptop can be in effect off.
Now, both modes take this into account and allow users to close the laptop without having to shut it down and close all apps and then wait for it to boot back up again.
First off, sleep mode supports instant startup as it makes use of the battery or power supply to suspend the RAM and keep all applications open and ready when sleep mode is deactivated.
While hibernation mode can’t support this, it is pretty fast in its resumption mode. This is because it has to move the memory from the hard disk back to the RAM. This usually takes a long time and largely depends on the speed of the permanent storage.
Now, since a system in sleep requires a power supply to preserve the RAM, a system in hibernation mode does not require power to suspend the memory on the RAM.
So let’s say the power source is removed or turned off; there could be data loss when a system is on sleep mode. Although, this is a rare occurrence with laptops as they have a battery pack. However, if the battery is removed while in sleep mode, there would be a data loss; however, this is not the case for a system in hibernation mode.
Hybrid Sleep
This is still similar to the hibernation mode, but the difference is that the system is put in a low power state like in sleep mode. However, all memory is stored on the permanent storage allowing for a faster resumption of work but not instantaneous. In the event of a loss of power, the storage is safe, and it can quickly be rewritten on the RAM when power is restored. Hibernation mode is useful when the laptop is not in use for long periods, but the sleep mode is useful for shorter periods between usage.
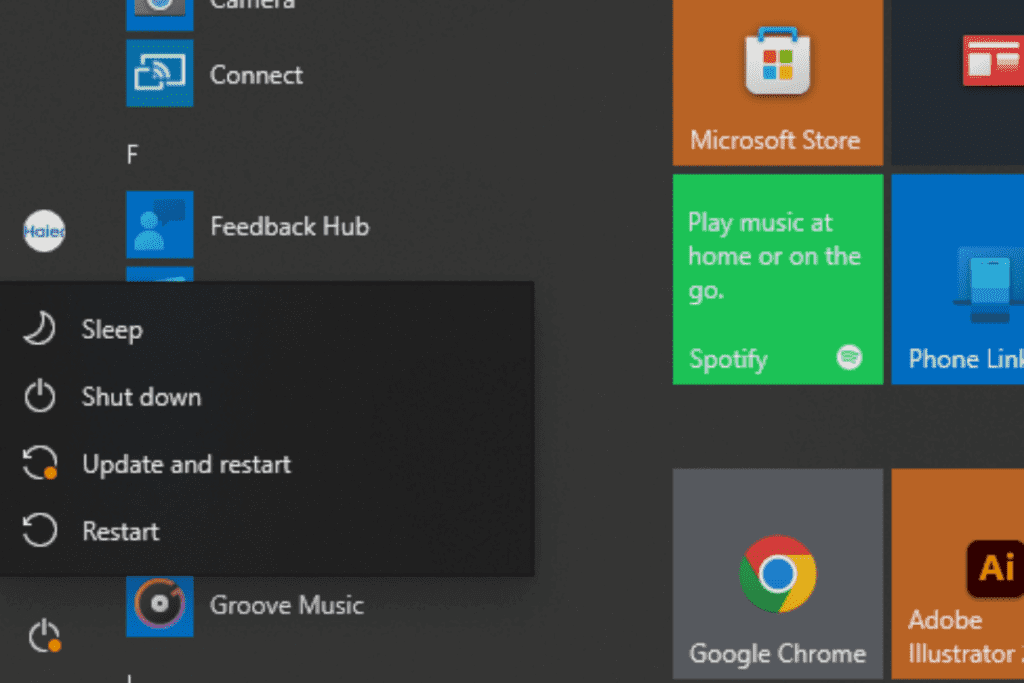
How To Put Your Computer Into Sleep or Hibernation Mode
On windows 10, both modes are accessed using the power button in the start menu. While on Windows 7, it is done by clicking the arrow next to the shutdown button on the start menu.
How to wake your device from either mode
You can wake your computer by pressing the power button. However, some computers may require you to press a key, click the mouse or trackpad, or even lift the lid of your laptop. You may need to refer to your laptop’s user manual or visit your computer manufacturer’s website for more specific info about waking from a power-saving state.
Is Sleep or Hibernation Mode Safe?
It is a good mode for saving power and getting back to work immediately after taking a break. It’s very helpful for workers who need to work quickly and remotely.
Conclusion
Hibernation mode is a power-saving state that allows a computer to quickly resume full-power operation (typically within several seconds) without going through a full reboot.
When hibernating, your computer will save any open documents and running applications to memory (RAM) and then turn off your computer.