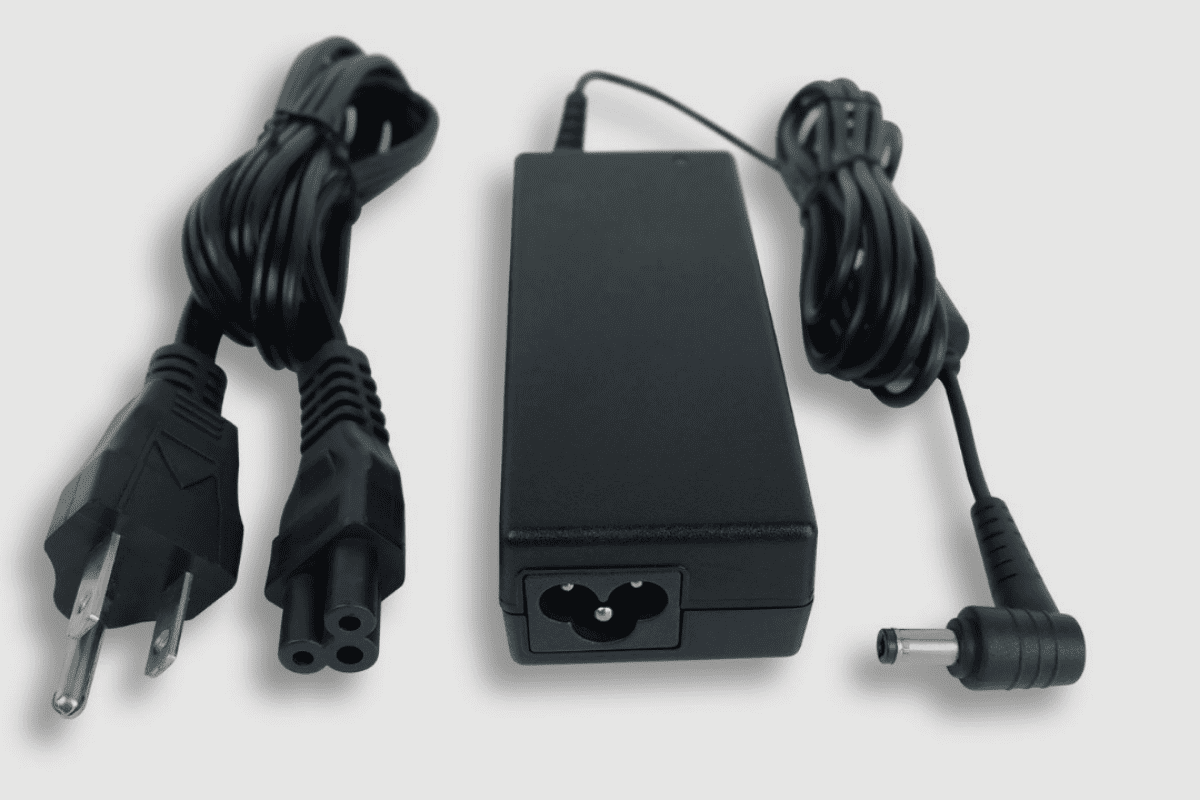
No, standard laptop chargers (AC adapters) don’t contain lithium batteries. Instead, they house a complex transformer system that converts high-voltage AC power from your wall outlet into the specific DC power your laptop needs.
What’s Actually Inside Your Laptop Charger
Your laptop charger contains several key components:
- Transformer: Converts high-voltage AC to lower-voltage AC
- Rectifier: Converts AC to DC power
- Voltage regulator: Ensures stable power output
- Safety circuits: Prevent overheating and power surges
- EMI filters: Reduce electromagnetic interference
Why This Matters for You
Understanding your laptop charger’s technology is crucial because:
- Safety: Without a battery buffer, your charger needs proper ventilation
- Performance: The right power output ensures optimal laptop battery health
- Cost: Knowing this helps you make informed decisions about replacements
- Lifespan: Proper care can extend your charger’s life significantly
The Common Misconception
Many people assume laptop chargers contain batteries because:
- They’re relatively heavy
- They sometimes feel warm
- They can “remember” voltage settings
- They often have LED indicators.
Real-World Applications
Understanding your charger’s technology helps you:
- Choose the right replacement: Match voltage and amperage exactly
- Prevent damage: Avoid covering the charger while in use
- Save money: Don’t pay extra for “battery-equipped” knockoffs
- Travel safely: Know which voltage ranges your charger supports.
Future Implications
While traditional laptop chargers don’t contain batteries, the future might be different:
- GaN Technology: New gallium nitride chargers are 40% smaller
- Power Banks: Hybrid charger-battery units are emerging
- Smart Charging: AI-powered adapters that optimize power delivery
- Universal Standards: USB-C PD is becoming the new norm.
Hidden Features You Didn’t Know About
Your laptop charger includes sophisticated protection:
- Over-voltage protection
- Short-circuit prevention
- Temperature monitoring
- Current limiting.

Practical Tips
- Keep it cool: Allow airflow around your charger
- Check compatibility: Match voltage/amperage when replacing
- Avoid cheap knockoffs: They may lack safety features
- Inspect regularly: Look for wear on cables and housing
Final Thought
The lack of a battery in laptop chargers is actually a smart design choice. It reduces weight, cost, and potential points of failure while maintaining efficiency. The transformer-based design has proven reliable for decades, though new technologies like GaN are revolutionizing the field.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Do laptop chargers contain lithium batteries inside them?
A: No, standard laptop chargers (AC adapters) do not contain lithium batteries. They are power conversion devices that transform AC power from wall outlets into DC power that your laptop can use. They contain transformers, capacitors, and other electronic components, but no batteries.
Q: What makes laptop chargers heavy if there’s no battery inside?
A: Laptop chargers are heavy due to their internal components, primarily the transformer which consists of copper coils and iron cores. These components are necessary for voltage conversion and maintaining electrical safety, regardless of whether a battery is present.
Q: Why does my laptop charger get warm during use if it has no battery?
A: The warmth comes from the power conversion process, not from a battery. When transforming high-voltage AC power to low-voltage DC power, some energy is naturally lost as heat through the transformer and other components. This is normal and expected behavior.
Q: Can I use my laptop charger without connecting it to a power outlet?
A: No, laptop chargers must be connected to a power outlet to function since they don’t contain batteries. They work by converting power from the wall outlet in real-time, rather than storing energy for later use.
Q: What’s the difference between a laptop charger and a power bank?
A: A laptop charger converts AC power to DC power but doesn’t store energy. A power bank contains lithium batteries that store energy for later use. While both can charge your laptop, they work differently – chargers need constant wall power, while power banks are portable energy storage devices.
Q: How long do laptop chargers last without batteries inside?
A: Quality laptop chargers typically last 3-5 years with proper care. Since they don’t contain batteries that degrade over time, their lifespan is determined by the durability of their electronic components and physical handling. Proper ventilation and careful cable management can extend their life significantly.
Q: Can a laptop charger work without its brick if it had a battery?
A: No, the power brick is essential for the charger to function as it contains the necessary components for power conversion. Even if it had a battery (which it doesn’t), the brick houses crucial transformation and safety components that can’t be bypassed.
Q: How can I tell if a laptop charger is genuine without checking for batteries?
A: Genuine laptop chargers can be identified by: official manufacturer branding, UL or similar safety certifications, correct weight (due to proper components), quality of construction, and accurate power specifications. The presence or absence of batteries is not a factor in determining authenticity.
Q: Why do some laptop chargers have LED lights if there’s no battery?
A: LED indicators on laptop chargers show the power status and connection health. They’re powered by the electrical current flowing through the charger, not by batteries. These lights help users verify if the charger is properly connected and functioning.
Q: Is it safe to use my laptop charger in different countries without a battery?
A: Most modern laptop chargers are dual-voltage capable (100-240V), making them safe for international use with the proper plug adapter. The lack of a battery doesn’t affect this capability, as it’s built into the charger’s power conversion circuitry.
Q: How do laptop chargers regulate power without battery storage?
A: Laptop chargers use sophisticated voltage regulators and capacitors to maintain stable power output. These components smooth out power fluctuations in real-time, without needing battery storage. The regulation happens through electronic circuits that monitor and adjust power flow continuously.
Q: Can wireless laptop chargers work without internal batteries?
A: Yes, wireless laptop chargers work through electromagnetic induction, not stored battery power. They still need to be plugged into a power outlet and contain similar power conversion components as traditional chargers, just with added induction coils for wireless power transfer.
Q: What happens if I cover my laptop charger since it has no battery?
A: Covering a laptop charger is dangerous regardless of battery presence. The power conversion process generates heat that needs to dissipate. Blocking ventilation can cause overheating, potentially damaging the charger or creating a fire hazard.
Q: Do new GaN laptop chargers contain batteries?
A: No, Gallium Nitride (GaN) laptop chargers don’t contain batteries either. They use advanced semiconductor technology to perform the same power conversion more efficiently, allowing for smaller size and less heat generation while still requiring constant wall power.
Q: Why do some chargers remember settings without batteries?
A: Chargers that “remember” settings use small electronic components like EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) chips, not batteries. These chips can retain information without power and use minimal energy from the charger when it’s plugged in.
Further Reading:
- “Understanding Power Adapters and Their Components” – Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI)
Link: https://www.esfi.org/understanding-your-home-electrical-system/. - “An Introduction to GaN Technology in Power Electronics” – IEEE Power Electronics Society
Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8932067.








