Over the years, Intel has built prestige for manufacturing the most trusted CPUs on the market. Intel processors are the most popular CPUs for desktops and laptops use in the world, and they come in a range of model names or brands, with “Core” being a model family name or brand.
Other model family names include Xeon, Pentium, and Celeron. The Core processors are the best set of processors produced by Intel for business and personal use.
In this article, you will learn everything about the Intel Core i3, i5, i7 and i9 processors. So that when next you get to choose an Intel Core CPU for your PC, you will be able to select the best one for your need.
- What Is The Difference Between Intel Core™ I3, I5, I7 And I9 Processors?
- What Are The Key Features Of Each Processor Type?
- What Are The Benefits Of Each Processor Type?
- What Are The Performance Differences Between The Processors?
- How Do The Processors Compare In Terms Of Power Consumption?
- What Are The Thermal Design Power (Tdp) Ratings For The Processors?
- What Are The Maximum Clock Speeds For The Processors?
- What Is The Difference In The Number Of Cores And Threads Between The Processors?
- What Is The Difference In The Cache Size Between The Processors?
- What Is The Difference In The Maximum Memory Support Between The Processors?
- What Is The Difference In The Maximum Memory Bandwidth Between The Processors?
- What Is The Difference In The Integrated Graphics Between The Processors?
- What Are The Security Features Of The Processors?
- What Are The Virtualisation Capabilities Of The Processors?
- What Are The Power Management Features Of The Processors?
- What Are The Thermal Management Features Of The Processors?
- What Are The Packaging And Socket Compatibility Considerations For The Processors?
- What Are The Pricing Considerations For The Processors?
- What Are The Warranty And Support Options For The Processors?
- Conclusion

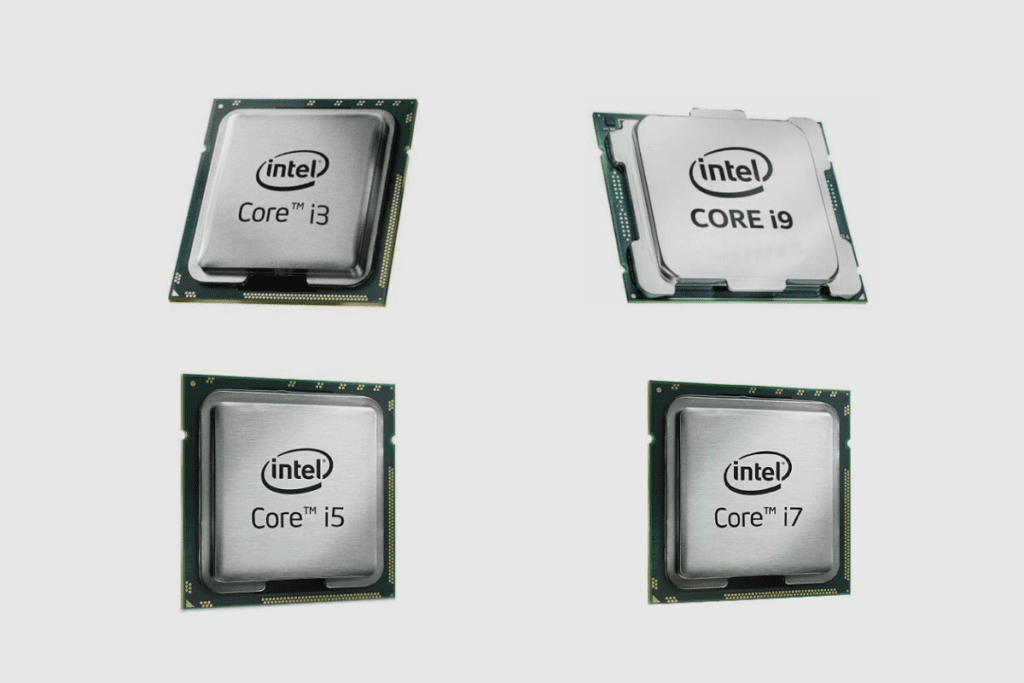
What Is The Difference Between Intel Core™ I3, I5, I7 And I9 Processors?
The Core brand of the processor is the only model family that comes with a brand modifier such as i3, i5, i7 and i9. The higher the modifier number, the better the performance and more features. The 3, 5, 7 and 9 attached to the brand of the Intel Core processors are mainly indicative of their processing power. Hence, an Intel Core i7 processor performs better than the Intel Core i5 processor.
Intel Core i3 is a great choice for low-cost PC and gaming desktops. If you are an everyday user, who just browses and streams media content, then the Intel Core i3 is great for you. The Intel Core i3 allows you to browse multiple web pages conveniently and use word processing applications and Excel. You can also listen to audio content from streaming platforms like Spotify. Generally, with the Intel Core i3, you can multi-task efficiently with the Intel Hyper-Threading technology.
The Intel Core i5 is more suitable for business use and for busy multitaskers like designers, photographers and PC gamers. With the Core i5 processor, you can multitask smoothly, work on complicated tasks like big Excel files; edit in Photoshop and sketch in Illustrator; create, share and watch content in 4k; play intensive PC games and stream from multiple sites. The Core i5 processor also gives you a temporary boost when using demanding programs with the Intel Turbo Boost Technology 2.0.
If you crave more performance power and good graphics, then the Intel Core i7 processor is for you. An advanced video editor, 3D modeller and gamer should consider the Core i7 processor as it has enough power for the most demanding tasks. With the Core i7 processor, you can encode videos more efficiently, work smoothly in 3D modelling programs, and watch and edit 4K UHD contents and 360° videos. You can work more productively with demanding creative programs and carry out faster-repeated tasks with the Intel Core i7 processor, thanks to the large cache size.
The Intel Core i9 processor is for extreme gaming, mega-tasking and high-end content creation. The Core i9 elevates your PC to a studio; you can produce astonishing 4K or 360° videos, stunning photos and high-quality music. For Gamers, the Core i9 is the ultimate tool for the virtual reality gaming experience.
What Are The Key Features Of Each Processor Type?
The Intel Core i3 processors are the lighter weight of the model family. The Core i3 processor comes in multiple speeds, ranging from 1.30 gigahertz (GHz) to 3.50 GHz, though there are advancements in this aspect. They also feature either 3 or 4 MB of cache and utilise the LGA 1150 or LGA 1155 socket on a motherboard. Core i3 processors are mostly found as a dual-core, that is, having two cores; however, few high-end Core i3 processors are quad-core, featuring four cores. Some also come with the Intel Hyper-Threading technology, which delivers two processing threads per physical core.
As regards the RAM, the most common type associated with the Core i3 processors is the DDR3 1333 or DDR3 1600. The Core i3 processors are also known for their lower heat generation and conservative battery usage. Your laptop can be used for up to five or six hours on a single battery charge when running on a Core i3 processor.
The Intel Core i5 processors are mostly available as quad-core, having four cores, with a select few high-end Core i5 processors featuring six cores. The Core i5 processor comes in multiple speeds, ranging from 1.90 GHz up to 3.80 GHz and features 3, 4 or 6 MB of cache and utilises either the LGA 1150 or LGA 1155 socket on the motherboard. The DDR3 1333 or DDR3 1600 are the common types of RAM associated with the Core i5 processors. However, a higher-performing RAM can be used if supported by the motherboard. The Core i5 processor also has a conservative battery usage. You can use your device for up to five hours on a single charge when used at a lower speed. At higher speeds, the battery can last up to three hours per charge.
Intel Core i7 processors feature four or six cores, with stock frequencies between 2.6 and 3.7 GHz. An interesting fact is that some Core i7 processors can be unlocked for overclocking – that is performing better than the advertised speed. The Core i7 processor is primarily manufactured for gaming enthusiasts and digital artists such as filmmakers and animators.
For the Intel Core i9 processors, they feature as few as six and as many as eighteen cores. When hyperthreading is enabled, it is two threads per core. The frequencies range from 2.9 to 3.6 GHz and up to 5.0 GHz when using Intel Turbo Boost. All Core i9 processors interface with a new Intel socket type, LGA 2066, making them not compatible with the previous generation motherboards.
What Are The Benefits Of Each Processor Type?
Here are the benefits of each of the processor types:
- The Intel Core i3 is an affordable processor that makes devices available to the mass market. It is also decent for general use and handles basic functions such as word processing and browsing. The Core i3 is also known for its low power consumption and battery efficiency. It uses less power than the rest.
- The Intel Core i5 performs the same tasks faster when compared to the Core i3. Your system is able to perform at the maximum CPU rate of 3.6 GHz. Also, the Core i5 has the Turbo technology that helps boost your device’s working speed and offers the 64-bit architecture that ensures reliable working.
- The benefits of the Core i7 processors include; first, it is the ideal processor for gamers and digital artists, with its fast processing speed and reliable cooling system. Its four cores also allow for the operation of the software that requires lots of computations. A major benefit is a provision of high data visualisation to users for high-quality images and video graphics.
- With the Intel Core i9 processors, you have the most powerful processor in the Intel Core model family, capable of high-definition gaming, high-resolution and multi-tasked video and audio editing, and the simultaneous use of resource-intensive applications.
What Are The Performance Differences Between The Processors?
When it comes to performance, there are differences between the processors.
The typical Intel Core i3 processor’s speed ranges from 1.30 gigahertz (GHz) to 3.50 GHz, and it also includes the turbo boost to enhance performance when needed. For the Intel Core i5, the processor comes in multiple speeds, ranging from 1.90 GHz up to 3.80 GHz.And it also has the
Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 gives you a temporary boost when using demanding programs.
The Intel Core i7 processor has stock frequencies between 2.6 and 3.7 GHz and can be unlocked for overclocking – that is performing better than the advertised speed. For the Intel Core i9 processors, the frequencies range from 2.9 to 3.6 GHz and up to 5.0 GHz when using Intel Turbo Boost.
The rule of thumb is that the higher the modifier number, the better the performance.
How Do The Processors Compare In Terms Of Power Consumption?
The Processors vary in terms of power consumption.
For the Intel Core i3, the power usage depends on the speed. Slower speeds (1.30 GHz to 1.80 GHz) use 11.5 Watt, 15 Watt or 25 Watt of power. Medium speeds use 28 Watt, 35 Watt or 37 Watt of power. For the faster speeds (2.90 GHz to 3.50 GHz), it varies between 35 Watt, 37 Watt or 54 Watt of power.
Power usage also varies for the Intel Core i5 processors depending on the speeds. The slower speeds (1.90 GHz to 2.30 GHz) use 11.5 Watt of power. The medium speeds (2.60 GHz to 3.10 GHz) use 15 Watt, 25 Watt, 28 Watt or 37 Watt of power. The faster speeds (3.20 GHz to 3.80 GHz) use 35 Watt, 37 Watt, 45 Watt, 47 Watt, 65 Watt or 84 Watt of power.
The Intel Core i7 uses at least 65 Watts but draws up to 215 Watts at peak power. For the Core i9, due to its high-performance rate, it consumes at least 154 Watt and up to 328 Watt at peak.
What Are The Thermal Design Power (Tdp) Ratings For The Processors?
The thermal design power (TDP) refers to the maximum amount of heat generated by the processor that the cooling system in a computer is designed to fritter way under any workload.
The Intel Core i3 has an average TDP of 35 watts under normal usage and a max of 69 watts when using the Intel Turbo boost. The Intel Core i5 has a base TDP of 65 watts, with a 154 TDP rating during boost.
The Core i7, depending on the workload, has a base TDP rating of 35-99 watts. At the same time, the Intel Core i9 processor has a base TDP rating of 125 watts and a max turbo TDP of 241 watts.

What Are The Maximum Clock Speeds For The Processors?
Taking cognisance of the latest versions of these processors, the Core i3 has a maximum clock speed of 4GHz, with the maximum turbo speed at 4.6GHz.
Core i5 processors have a maximum clock speed of 3.7GHz, with the maximum Turbo speed at 4.6GHz. The Core i7 processor has its maximum clock speed at 3.6GHz, while the Turbo peak sits at 4.9GHz.
The Intel Core i9 processor is claimed to be the fastest, with a maximum clock speed between 5GHz – 5.5 GHz, depending on the model.
What Is The Difference In The Number Of Cores And Threads Between The Processors?
What you should know is that the more cores a processor has, the more tasks (known as threads) can be done at the same time. Then, you are more likely to find less cores in a Core i3 than in a Core i5 or Core i7.
Most Intel Core i3 processors have two cores and two threads per core, making it four threads. However, you can find some new Intel Core i3 processors with four cores and four threads.
Most Intel Core i5 processors have been built on four cores, but recent models have six cores. So the Core i5 can process at least eight threads at once. For the Core i7 processors, you would find some with four cores, but the modern models feature up to eight cores.
The Intel Core i9 processors are known to have at least eight cores, hence can process 16 threads at once. Interestingly, the Intel Core i9 is the first processor to feature a model with 18 cores and 36 threads.
What Is The Difference In The Cache Size Between The Processors?
The cache size refers to the amount of main memory data a processor can hold. The Intel Core i3 processor has 3-4 MB of cache size.
The Core i5 processors can be found with 3, 4 or 6 MB of cache size, depending on the model. For the Intel Core i7 processors, the least cache size you can find is 8 MB; you can find some with 12 MB.
The Intel Core i9 processors typically have a 16 MB cache size. But newer models are having of to 20 MB of cache size.

What Is The Difference In The Maximum Memory Support Between The Processors?
Maximum memory support refers to the short-term memory where data can be stored when the processor needs it.
The Intel Core i3 processors are typically known to support no more than 16 GB. But there are modern models that can support up to 32 GB to 64 GB of memory support.
For the Intel Core i5 processors, the maximum memory support is at least 16 GB, but they can support 32 GB, 64 GB and 128 GB, depending on the memory type.
The Core i7 processors have maximum memory support of at least 32 GB and depending on the model, and you can have up to 128 GB.
The maximum memory support for the Intel Core i9 begins from 64 GB, and you can also have it measure up to 128 GB.
What Is The Difference In The Maximum Memory Bandwidth Between The Processors?
The maximum memory bandwidth is the maximum rate at which data can be read from or stored into a semiconductor memory by the processor. It is measured in GB/s.
For the Intel Core i3 processors, the maximum memory bandwidth ranges from 21 GB/s to 25.6GB/s.
The maximum memory bandwidth for the Core i5 processor models is 34.1GB/s. For the Intel Core i7 processors, the maximum memory bandwidth ranges from 41.66GB/s – to 45.8GB/s, depending on the model.
The Core i9 processor has a maximum memory bandwidth of 41.66GB/s – 51.2GB/s, depending on the model.
What Is The Difference In The Integrated Graphics Between The Processors?
The integrated graphics is the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) built into the processor. The GPU is purely for graphics processing operations, and it helps to lighten the load on the Central Processing Unit (CPU), especially when a graphics-intensive game or application is running.
The Intel Core i3 uses the Intel UHD Graphics 630 chipset, which has a base clock of 340- 350 MHz. Some newer model uses the integrated Intel Graphics Media Accelerator HD (GMA HD) graphics card, which is known to be clocked up to 500-667 MHz.
The Intel Core i5 also utilises the UHD Graphics 630 chipset. You could find some with HD 530 chipset. Both most have a base clock of 350 MHz.
For the Intel Core i7 processors, a fair number of them support integrated graphics, while you could find some that do not come with integrated graphics. Those with integrated graphics use the Intel UHD Graphics 770 chipset with a base clock of 350 MHz.
The Intel Core i9 processors utilise the Intel UHD Graphics 630 chipset with a base clock of 350 MHz. You could also find some models of the Core i9 with an integrated Intel UHD 770 Graphics chipset.
What Are The Security Features Of The Processors?
Intel Core processors come with some security features. On top of the list is the Intel OS Guard, also known as Supervisor-Mode Execution Prevention (SMEP) which does not allow the operating system to directly execute application code, even speculatively.
There is also the Control-Flow Enforcement Technology (CET) which allows limiting near indirect jump and call instructions. This helps to reduce your device’s space.
There is also the Supervisor-Mode Access Prevention (SMAP) that limits which memory addresses can be used for a cache-based side-channel by blocking the allocation of an application line.
The interesting thing is that Intel keeps upgrading the security features of its processors.
What Are The Virtualisation Capabilities Of The Processors?
What virtualisation capability means is the ability to tune multiple operating systems on a single processor. The Intel Core processors support virtualisation on desktop PCs. But you might experience a lag when using the Core i3. Virtualisation is not to be taken for multitasking.
The higher the modifier number, the better suited the processor is suited for virtualisation.
What Are The Power Management Features Of The Processors?
The Power management feature allows you to control the amount of electrical power consumed by your device with minimal impact on performance. And also for longer battery life.
The Intel Core processors contain the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) that helps you manage your device’s battery life. The ACPI affords you the opportunity to put your device to sleep or in hibernation mode. There is also the Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST) that helps with voltage scaling.
What Are The Thermal Management Features Of The Processors?
Thermal management simply means monitoring and controlling the temperatures produced by the processors. The goal is to keep the processor at or below its maximum operating temperature.
The Core processors come with a standard fan heatsink with thermal interface material pre-applied to the base. The thermal interface material (TIM) provides effective heat transfer from the processor to the fan heatsink, and you have to ensure that it is correctly applied before installing the processor. There is also an attached fan cable to provide power to the fan that provides fan speed information to the motherboard.
One thing you must know is that the temperature operations of each processor vary as it depends on the system design and workload. But the Core processors have an inbuilt system to manage the temperature.
What Are The Packaging And Socket Compatibility Considerations For The Processors?
For packaging, Intel utilises the Land Gray Array (LGA) CPU sockets. And the LGA has been upgraded over the years, with more pins and designs to expand functionality.
The Intel Core i3 processors mostly utilise the LGA 1150 or LGA 1155 socket on the motherboard. For the Intel Core i5, it is the LGA 1150 or LGA 1155 socket on the motherboard.
The Intel Core i7 processors utilise the LGA 1156, LGA 1700, or LGA 1200, depending on the model.
For the Core i9 processor, the supported socket is the LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4.
What Are The Pricing Considerations For The Processors?
From the features of the various core processors explained so far, it is clear that devices with a higher modifier core processor tend to be more expensive than the other.
What you should consider before opting for a particular core processor type is what you intend to use the computer to do, the type of software to be run, the processor compatibility, the number of cores needed and the speed of the processor.
What Are The Warranty And Support Options For The Processors?
Intel typically places a three-year warranty period on their processors. And it starts on the original purchase date and does not apply again if Intel provides a replacement. Also, the warranty does not apply to grey-market, second-hand, gifted, or products not purchased from authorised distributors or resellers. And warranty requests for products identified as counterfeit or remarked are not honoured.
The support options available include a comparison of processors, troubleshooting actions, compatibility, how to deal with error messages, and how to install and set up.
Conclusion
Without a doubt, the Core family of the Intel processors are the most trusted and used, and the reasons for this are not far-fetched.
When it is time to pick up a device that has the Intel processor, I am sure you would know the right one to go for, depending on what you want to use your device to do.









